2023.08.19 : Note, I don’t use this setup anymore. Instead, I switched to a Raspberry Pico W. This new setup is not documented yet…
Thermostat
This is a personal project where I’m creating a smart thermostat. The idea is to make a dumb thermostat where you can change the setpoint over bluetooth. A small computer like the Raspberry Pi communicates with this dumb thermostat over bluetooth to make the dumb thermostat smart.
Theoretically it is possible to let just a computer like the Raspberry Pi control the heating, but I don’t trust computers enough to let them do the control directly. Think about things like sd-card or file system corruption, which on occasion can happen.
By making use of a dumb microcontroller based thermostat, it’s still possible to control the heating when the smart part fails.
1. pic18f1320 : dumb thermostat
- schematic diagram
- software, written in assembler (gpasm - GNU PIC assembler)
1.1. Configuration of the HC-05 Bluetooth module.
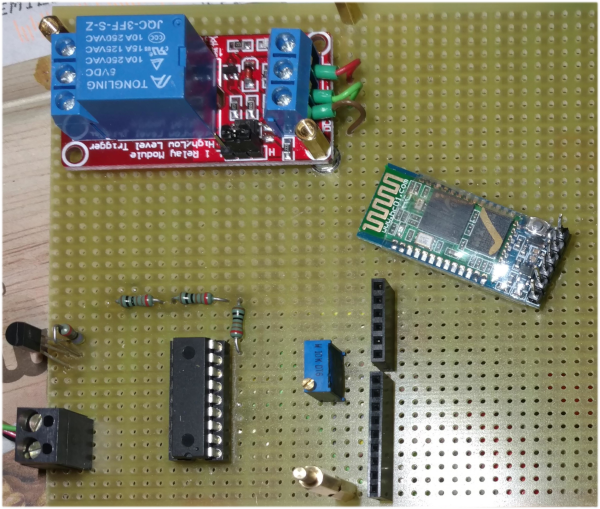
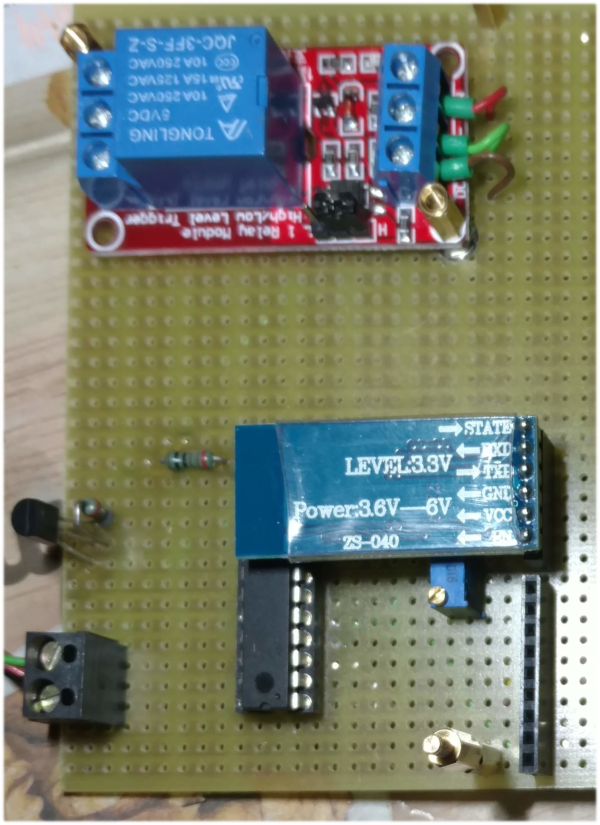
The pic18f1320 communicates with a HC-05 Bluetooth module at a speed of 2400 baud. To configure the HC-05:
- connect it to the serial port of a Raspberry Pi (/dev/ttyS0)
- put the HC-05 in “AT mode” by pressing it’s button.
- In a terminal program like minicom enter the command
AT+UART=2400,0,0.
It’s also a good idea to change the default password of the HC-05 by
entering the command AT+PSWD:4321. You can get the current password with
AT+PSWD?
1.2. Commands
By using a HC-05 Bluetooth module connected to the pic18f1320 microcontroller it’s possile to send commands to the thermostat.
The following commands are recognized by the thermostat:
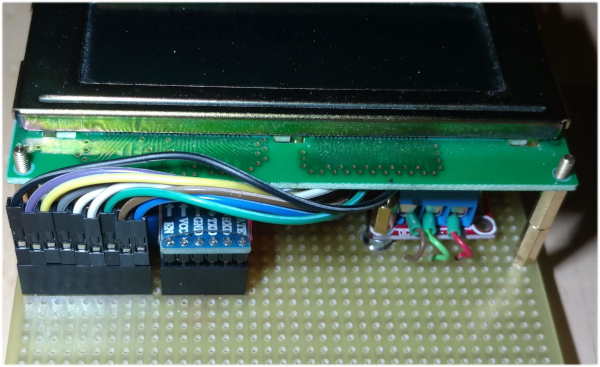
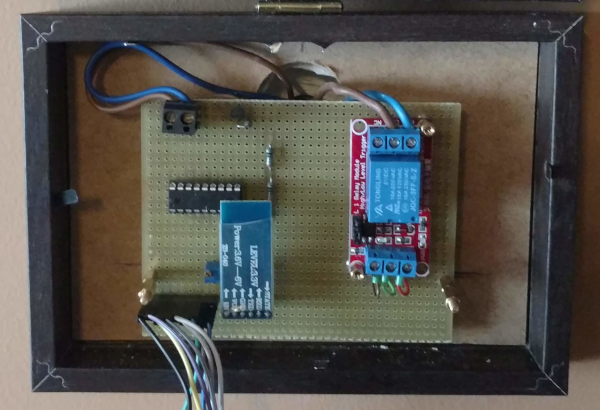
1.3. Pictures PCB
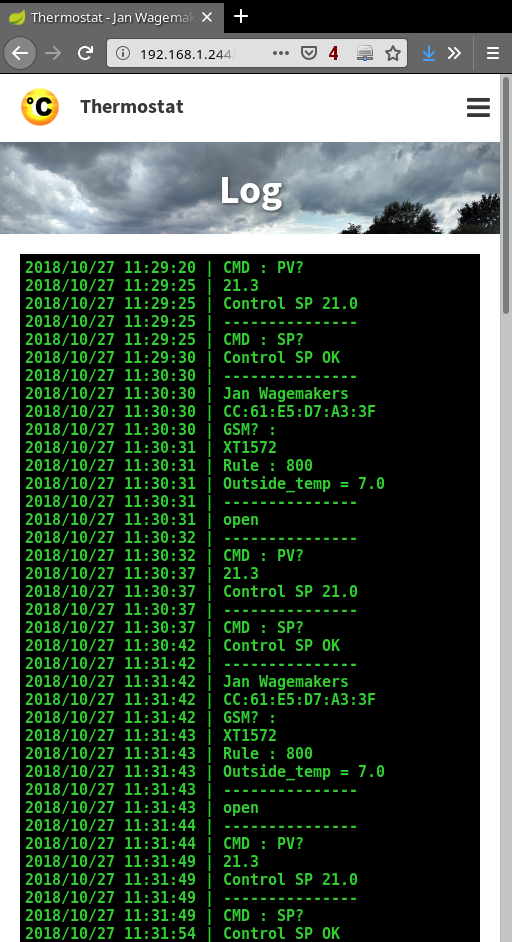
2. Raspberry Pi : smart thermostat
JAVA Spring Boot program that:
- communicates with dumb thermostat over bluetooth
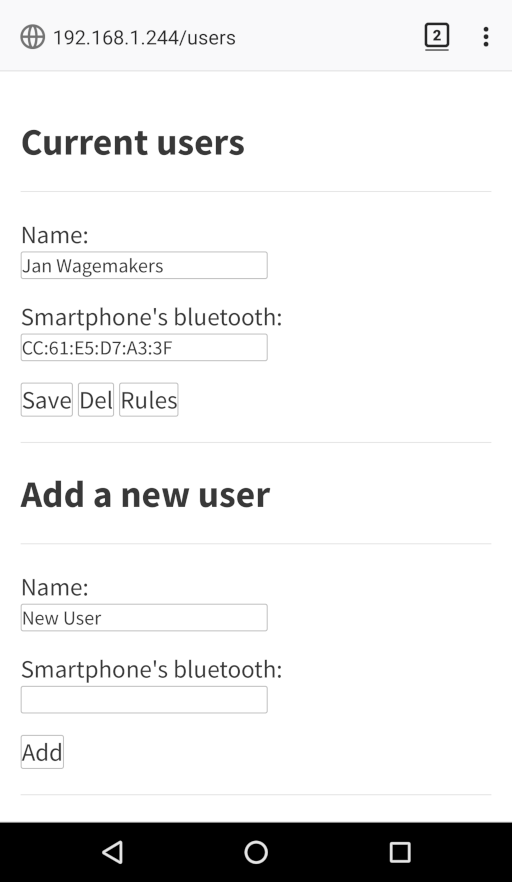
- checks if a user is home by checking smartphone/bluetooth or smartphone/IP-address
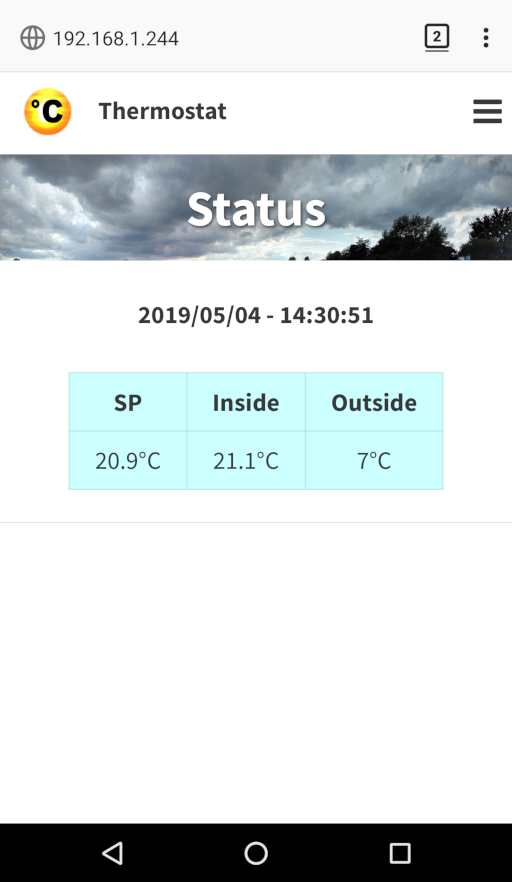
- creates a web interface at port 8080
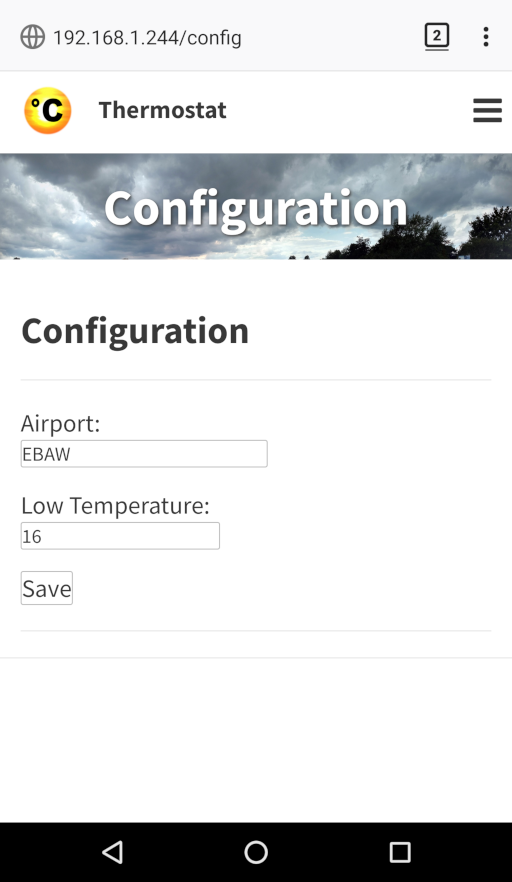
- reads the outside temperature and atmospheric pressure from https://tgftp.nws.noaa.gov/data/observations/metar/stations/
- use the outside temperature and atmospheric pressure to lower the setpoint if it’s warm outside
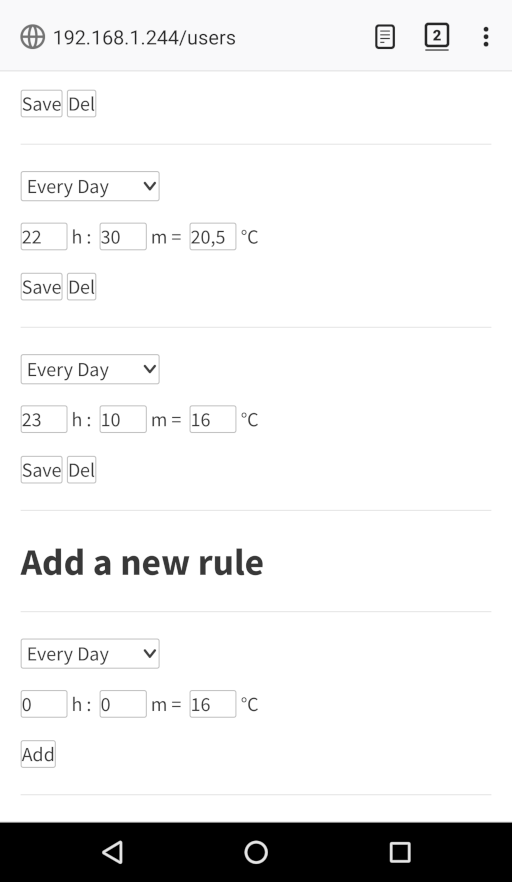
- it’s possible to add/delete/change “users”,”rules” and “configuration” by using the web interface
2.1. Configure Bluetooth
On a terminal enter the command bluetoothctl and then enter:
power on
agent on
scan on
pair xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
connect xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
trust xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
2.2. Configure the RFCOMM serial port
The communication over bluetooth works by the RFCOMM protocol. To set up
the RFCOMM serial port enter the command rfcomm bind 0 xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx.
Because after a reboot, you have to issue this command again, it’s a good
idea to include the following line in /etc/crontab:
@reboot root /usr/bin/rfcomm bind 0 xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
To test the communication, use the command minicom -D /dev/rfcomm0
2.3. hcitool : detect smartphone
To detect a smartphone by Bluetooth (to check if somebody is home), hcitool is used. To be able to run hcitool without being root, enter the command:
sudo setcap 'cap_net_raw,cap_net_admin+eip' `which hcitool`
2.4. systemd : start thermostat at boot
Create a file /etc/systemd/system/thermostat.service with the following
content:
# /etc/systemd/system/thermostat.service
[Unit]
Description=thermostat
After=syslog.target
[Service]
User=your_username
Restart=always
RestartSec=3
ExecStart=/usr/bin/java -jar /home/your_username/thermostat.jar
StandardOutput=journal
StandardError=journal
SyslogIdentifier=thermostat
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Then, in a terminal enter the following commands:
systemctl start thermostat.service
systemctl enable thermostat.service
3. Source
https://gitlab.com/jan.wagemakers/thermostat/
4. Demo
A demo version of the web interface is available at http://janw.mooo.com:24388.
Note that in this demo version it’s not possible to change the database (“rules”, “users”, “configuration”). The current temperature it shows is just a random value. It’s just there to show the current interface.